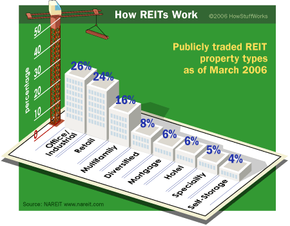
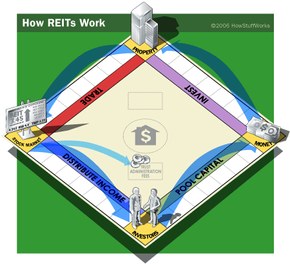
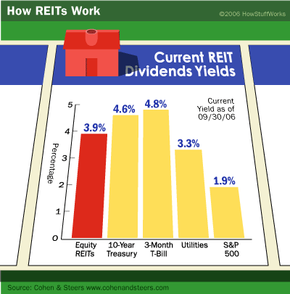
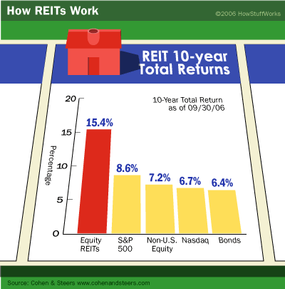
Investing in income-generating real estate can be a great way to increase your net worth. But for many people, investing in real estate, particularly commercial real estate, is simply out of reach financially. But what if you could pool your resources with other small investors and invest in large-scale commercial real estate as a group? REITs (pronounced like "treats") allow you to do just that.
REIT stands for real estate investment trust and is sometimes called "real estate stock." Essentially, REITs are corporations that own and manage a portfolio of real estate properties and mortgages. Anyone can buy shares in a publicly traded REIT. They offer the benefits of real estate ownership without the headaches or expense of being a landlord.
Advertisement
Investing in some types of REITs also provides the important advantages of liquidity and diversity. Unlike actual real estate property, these shares can be quickly and easily sold. And because you're investing in a portfolio of properties rather than a single building, you face less financial risk.
REITs came about in 1960, when Congress decided that smaller investors should also be able to invest in large-scale, income-producing real estate. It determined that the best way to do this was the follow the model of investing in other industries -- the purchase of equity.
A company must distribute at least 90 percent of its taxable income to its shareholders each year to qualify as a REIT. Most REITs pay out 100 percent of their taxable income. In order to maintain its status as a pass-through entity, a REIT deducts these dividends from its corporate taxable income. A pass-through entity does not have to pay corporate federal or state income tax -- it passes the responsibility of paying these taxes onto its shareholders. REITs cannot pass tax losses through to investors, however.
From the 1880s to the 1930s, a similar provision was in place that allowed investors to avoid double taxation -- paying taxes on both the corporate and individual level -- because trusts were not taxed at the corporate level if income was distributed to beneficiaries. This was reversed in the 1930s, when passive investments were taxed at both the corporate level and as part of individual income tax. REIT proponents were unable to persuade legislation to overturn this decision for 30 years. Because of the high demand for real estate funds, President Eisenhower signed the 1960 real estate investment trust tax provision qualifying REITs as pass-through entities.
A corporation must meet several other requirements to qualify as a REIT and gain pass-through entity status. They must:
- Be structured as corporation, business trust, or similar association
- Be managed by a board of directors or trustees
- Offer fully transferable shares
- Have at least 100 shareholders
- Pay dividends of at least 90 percent of the REIT's taxable income
- Have no more than 50 percent of its shares held by five or fewer individuals during the last half of each taxable year
- Hold at least 75 percent of total investment assets in real estate
- Have no more than 20 percent of its assets consist of stocks in taxable REIT subsidiaries
- Derive at least 75 percent of gross income from rents or mortgage interest
At least 95 percent of a REIT's gross income must come from financial investments (in other words, it must pass the 95-percent income test). These include include rents, dividends, interest and capital gains. In addition, at least 75 percent of its income must come from certain real estate sources (the 75-percent income test), including rents from real property, gains from the sale or other disposition of real property, and income and gain derived from foreclosure of property.
We'll look at the different types of REITs next.
Advertisement