Down the Tubes
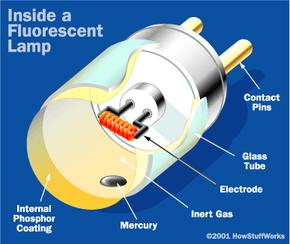
The central element in a fluorescent lamp is a sealed glass tube. The tube contains a small bit of mercury and an inert gas, typically argon, kept under very low pressure. The tube also contains a phosphor powder, coated along the inside of the glass. The tube has two electrodes, one at each end, which are wired to an electrical circuit. The electrical circuit, which we'll examine later, is hooked up to an alternating current (AC) supply.
When you turn the lamp on, the current flows through the electrical circuit to the electrodes. There is a considerable voltage across the electrodes, so electrons will migrate through the gas from one end of the tube to the other. This energy changes some of the mercury in the tube from a liquid to a gas. As electrons and charged atoms move through the tube, some of them will collide with the gaseous mercury atoms. These collisions excite the atoms, bumping electrons up to higher energy levels. When the electrons return to their original energy level, they release light photons.
Advertisement
As we saw in the last section, the wavelength of a photon is determined by the particular electron arrangement in the atom. The electrons in mercury atoms are arranged in such a way that they mostly release light photons in the ultraviolet wavelength range. Our eyes don't register ultraviolet photons, so this sort of light needs to be converted into visible light to illuminate the lamp.
This is where the tube's phosphor powder coating comes in. Phosphors are substances that give off light when they are exposed to light. When a photon hits a phosphor atom, one of the phosphor's electrons jumps to a higher energy level and the atom heats up. When the electron falls back to its normal level, it releases energy in the form of another photon. This photon has less energy than the original photon, because some energy was lost as heat. In a fluorescent lamp, the emitted light is in the visible spectrum -- the phosphor gives off white light we can see. Manufacturers can vary the color of the light by using different combinations of phosphors.
Conventional incandescent light bulbs also emit a good bit of ultraviolet light, but they do not convert any of it to visible light. Consequently, a lot of the energy used to power an incandescent lamp is wasted. A fluorescent lamp puts this invisible light to work, and so is more efficient. Incandescent lamps also lose more energy through heat emission than do fluorescent lamps. Overall, a typical fluorescent lamp is four to six times more efficient than an incandescent lamp. People generally use incandescent lights in the home, however, since they emit a "warmer" light -- a light with more red and less blue.
As we've seen, the entire fluorescent lamp system depends on an electrical current flowing through the gas in the glass tube. In the next section, we'll see what a fluorescent lamp needs to do to establish this current.