Hot water and steam systems work similarly, but neither are typically installed in newer homes. However, because both are still in existing homes, here are some maintenance tips for them.
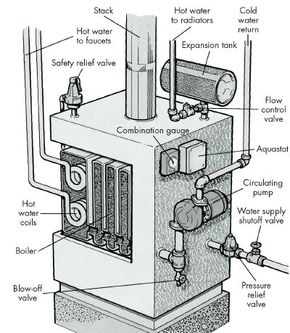
Because water retains heat, it is used to store and distribute heat in home systems. There are two types of hot water systems: the gravity system and the hydronic or forced hot water type. Hot water heating systems can be powered by gas, oil, or electricity.
Advertisement
Gravity systems depend on the upward flow of hot water to circulate heated water from the boiler through a system of pipes to radiators in the rooms of your home. The better radiators for hot water systems are called convectors. These units employ a series of fans to disperse the heat.
The heat from the water in the radiators or convectors is transferred first to the metal radiators and then to the air. As the water loses its heat, it sinks and flows back to the boiler through return pipes. Most gravity systems heat the water to no more than about 180 degrees Fahrenheit, and cooled water that goes back to the boiler rarely falls below 120 degrees Fahrenheit.
Open gravity systems have an overflow outlet to let water escape; this prevents a buildup of excess pressure in the system. Closed systems have a sealed expansion tank; when water pressure builds up in the system, the excess water flows into the expansion tank to prevent damage to the pipes or the boiler. Hydronic hot water systems are much like closed gravity systems, except a hydronic system uses a motor-driven circulating pump to move the water. As a result, water in a hydronic system moves more rapidly and arrives at the room radiator with less heat loss than water in a gravity system.
There are other key factors to consider when maintaining a hot water and steam distribution system. Learn these maintenance guidelines in the next section.
Advertisement